
You should see the login prompt ( Figure A), where you can create a new account.įigure A The Bitwarden server login prompt.īefore you create your account, you’ll need to first configure SMTP.
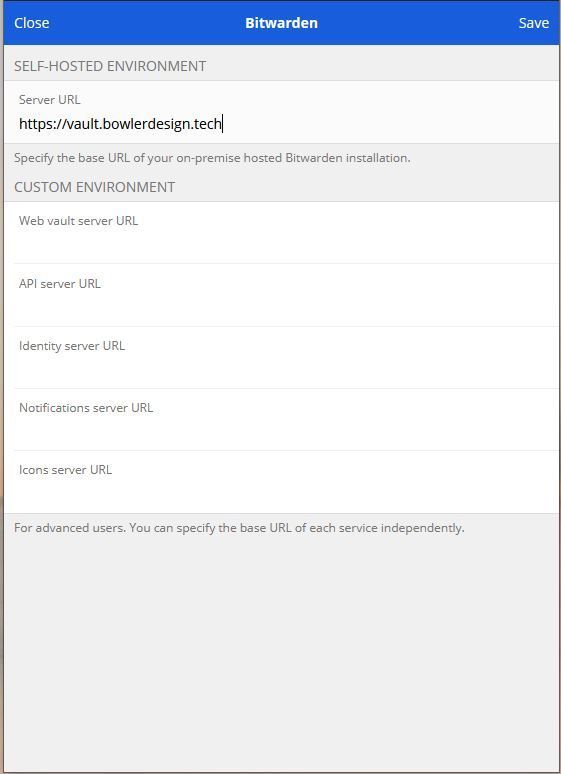
When the start command completes, you should be able to open a browser and point it to where SERVER is the IP address or domain of the hosting server. When that command completes, start the server with: You can access those keys from the Bitwarden host page, where you’ll be asked to enter an email address. During the installation, you’ll be asked for your installation ID and key. Once the file has been downloaded, launch it with:Īnswer the required questions - such as domain and SSL details - and the script will then start pulling down the required Docker images. Thankfully, the developers of Bitwarden have created a handy installation script, which you can download with the command:Ĭurl -Lso bitwarden.sh & chmod 700 bitwarden.sh Sudo chown -R bitwarden:bitwarden /opt/bitwarden Set the permissions and ownership of the new directory with:
#Self hosted bitwarden how to#
How to deploy the Bitwarden serverīefore we install, let’s create a new user with the command: Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect. Make sure your user is a member of the docker group with the command:
#Self hosted bitwarden install#
Sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y Sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release -yįinally, we can install the latest version of the Docker engine: Install the necessary dependencies with the command:
#Self hosted bitwarden software#
First, add the GPG key with the command:Ĭurl -fsSL | sudo gpg -dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg Open source: Must-read coverageĦ Best Linux project management software in 2023Ħ best open-source kanban boards for managing projects in 2023Ħ Best Free Alternatives to Microsoft Word (2023 Update)Įcho "deb $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt//docker.list > /dev/null The first thing we’ll do is install the latest release of Docker. I’ll be demonstrating on an instance of Ubuntu Server 22.04, but you can deploy the Bitwarden vault server on any platform that supports Docker. If that’s the case, why worry that data will be stored on a third-party host? What you’ll need to deploy a Bitwarden server Why would you want to deploy your own Bitwarden server? You might have incredibly sensitive information that you only entrust to your internal teams. SEE: Password breach: Why pop culture and passwords don’t mix (free PDF) (TechRepublic) One of the many reasons why this is so is because of the tool’s flexibility, and a perfect illustration of that is the ability to deploy your very own Bitwarden server using Docker. I might even go so far as to say it’s the best password manager period. Image: STOATPHOTO/Adobe Stockīitwarden is one of the best open-source password managers on the market.

Jack Wallen walks you through the process of deploying a Bitwarden vault server with the help of Docker containers. How to deploy the Bitwarden self-hosted server with Docker


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
